Compensating BNC Oscilloscope Probes

Overview
BNC oscilloscope probes are commonly used for analog inputs on many oscilloscopes, offering both the ability to read higher voltages than an oscilloscope natively supports as well as higher bandwidth, providing users better insight into the high-speed signals they are observing with much more accuracy than what is offered by MTE cables. However, as the 10x mode of the BNC probe adds extra resistance to correspondingly attenuate the input signal down by a factor of 10, the capacitance of the BNC probe is not likely to match the capacitance of the analog input channel you are using, resulting in the measured signal to be over- or under-compensated rather than accurately showing the signal you are viewing. Luckily, this can be mitigated by adjusting the capacitance of the BNC probe.
This guide walks through how to make this adjustment for Digilent's Test and Measurement devices.
Inventory
- A BNC probe to be compensated
- This guide will use the BNC probes kitted and included with Digilent's various T&M devices.
- An oscilloscope with a BNC connectors:
- A square wave source:
- Analog Discovery Pro (ADP5250) features dedicated Probe Compensation tabs
- For other devices, the built-in Arbitrary Waveform Generator can be used to produce 5 kHz square waves
- An example WaveForms workspace to compensate a BNC probe on Scope Channel 1 is available for download here.
- A flathead screwdriver to adjust the compensation trimmer on the BNC probe
- A small plastic screwdriver is typically included with BNC probe packs.
Guide
This guide is broken up into sections for each type of device that might require probe compensation. Open the dropdown corresponding to your device to view the required steps.
Hardware Setup
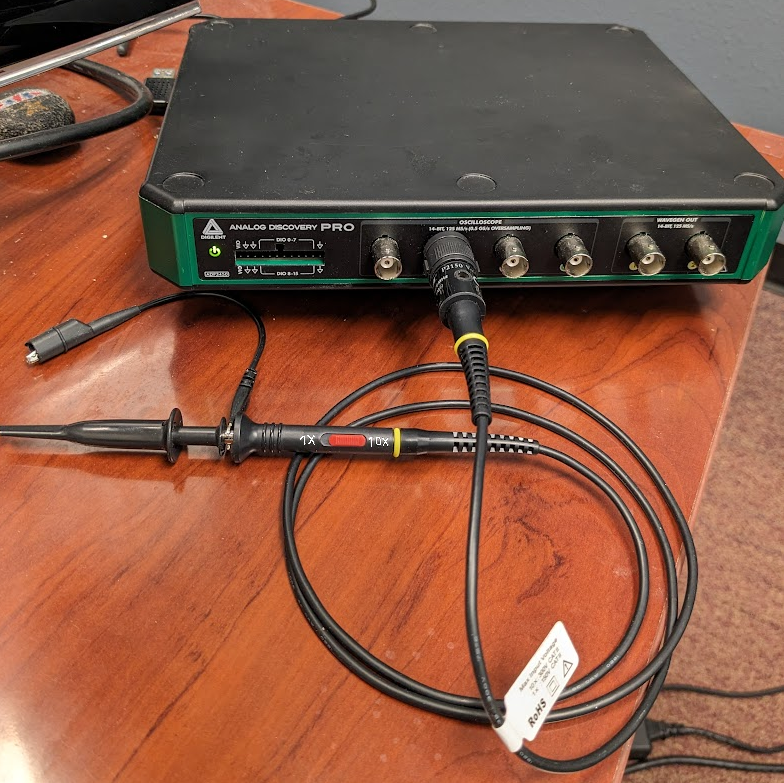
- Analog Discovery Pro 2000 Series (ADP2230)
-
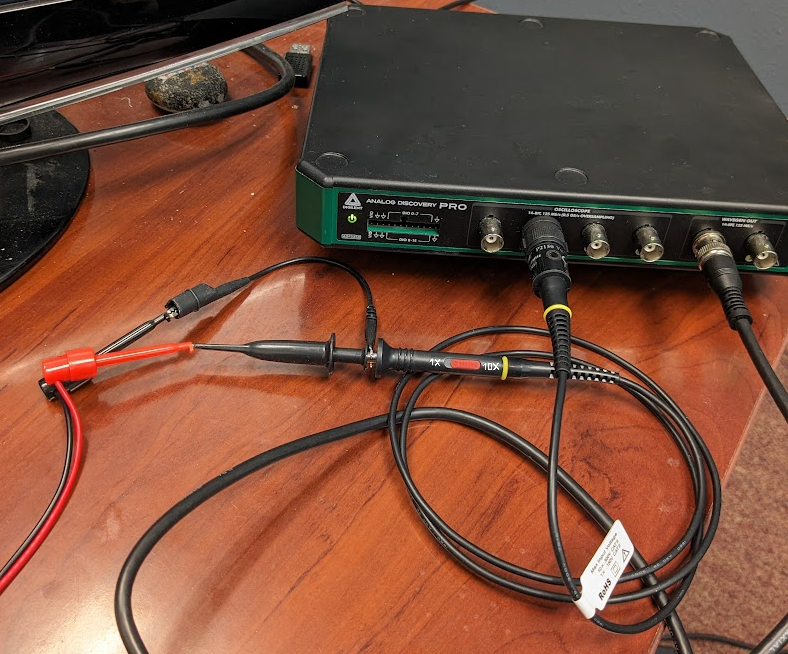
- Analog Discovery Pro 3000 Series (ADP3450/ADP3250)
-
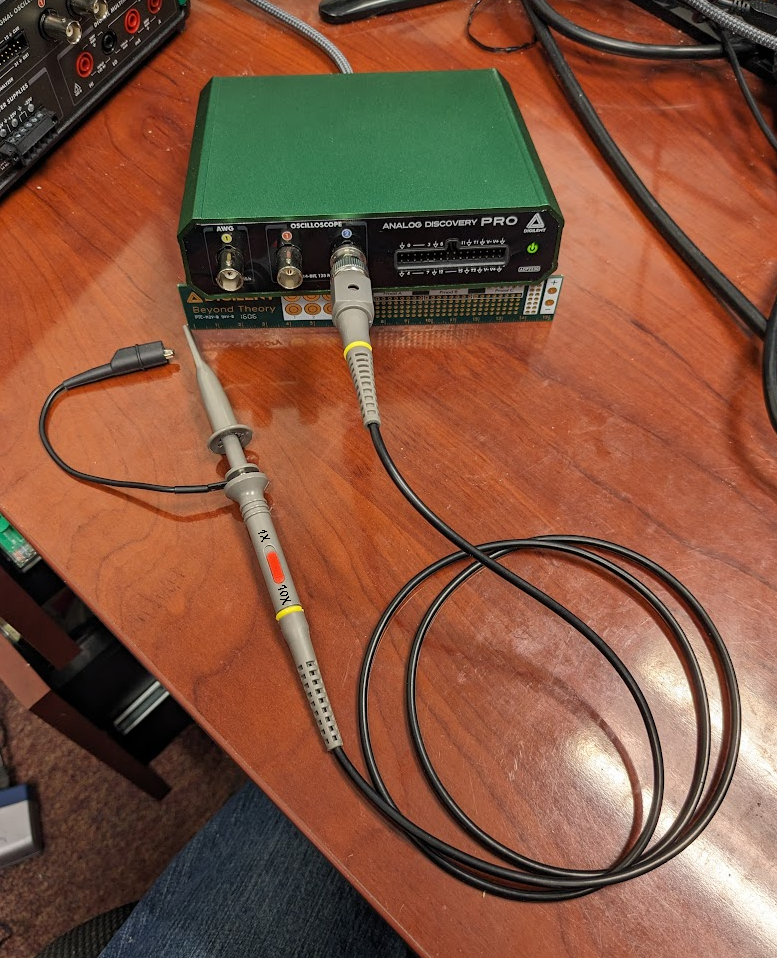
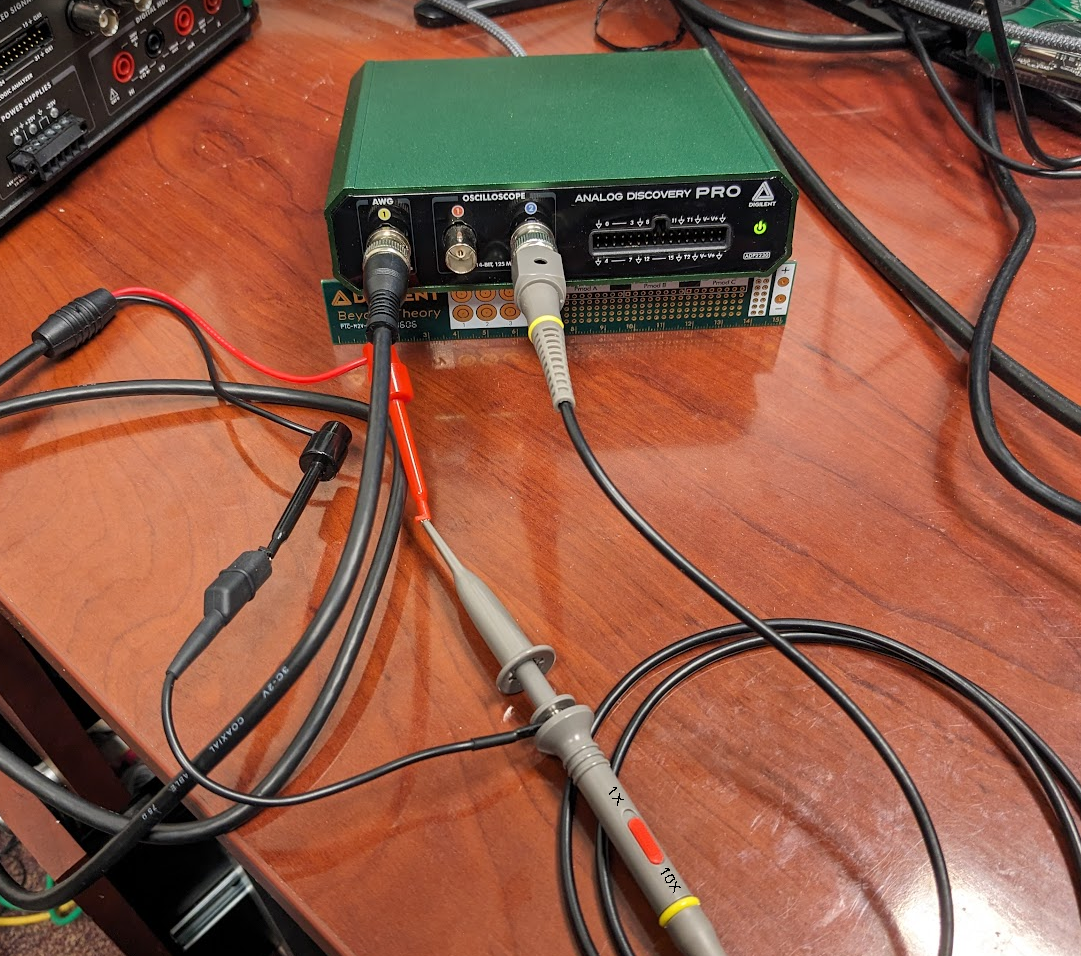
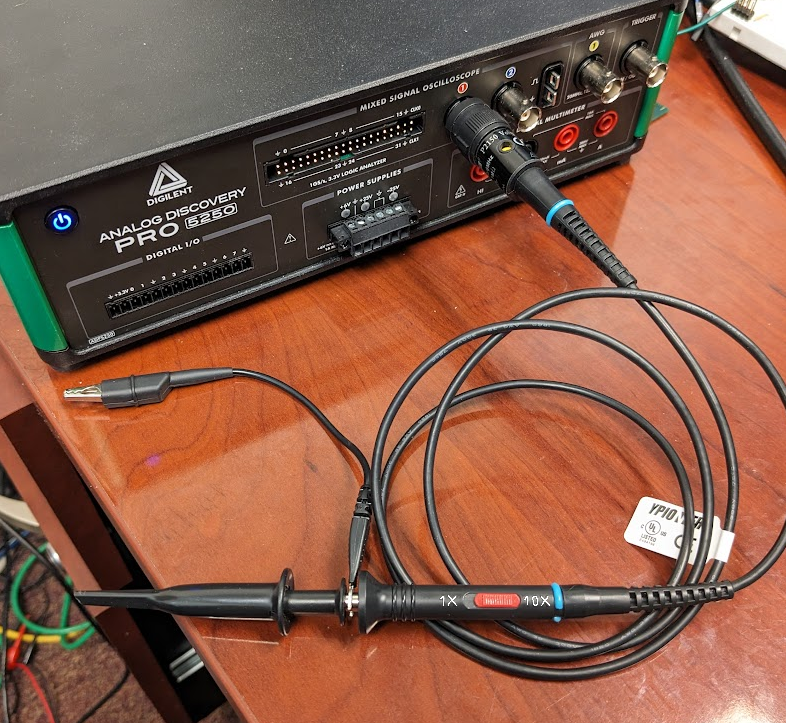
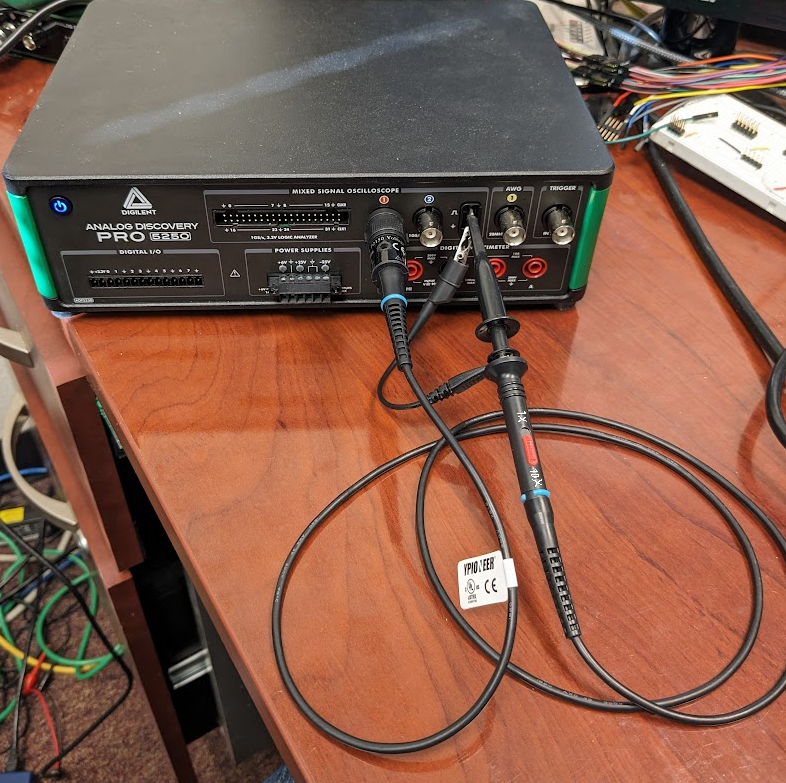
- Analog Discovery Pro 5000 Series (ADP5250)
-
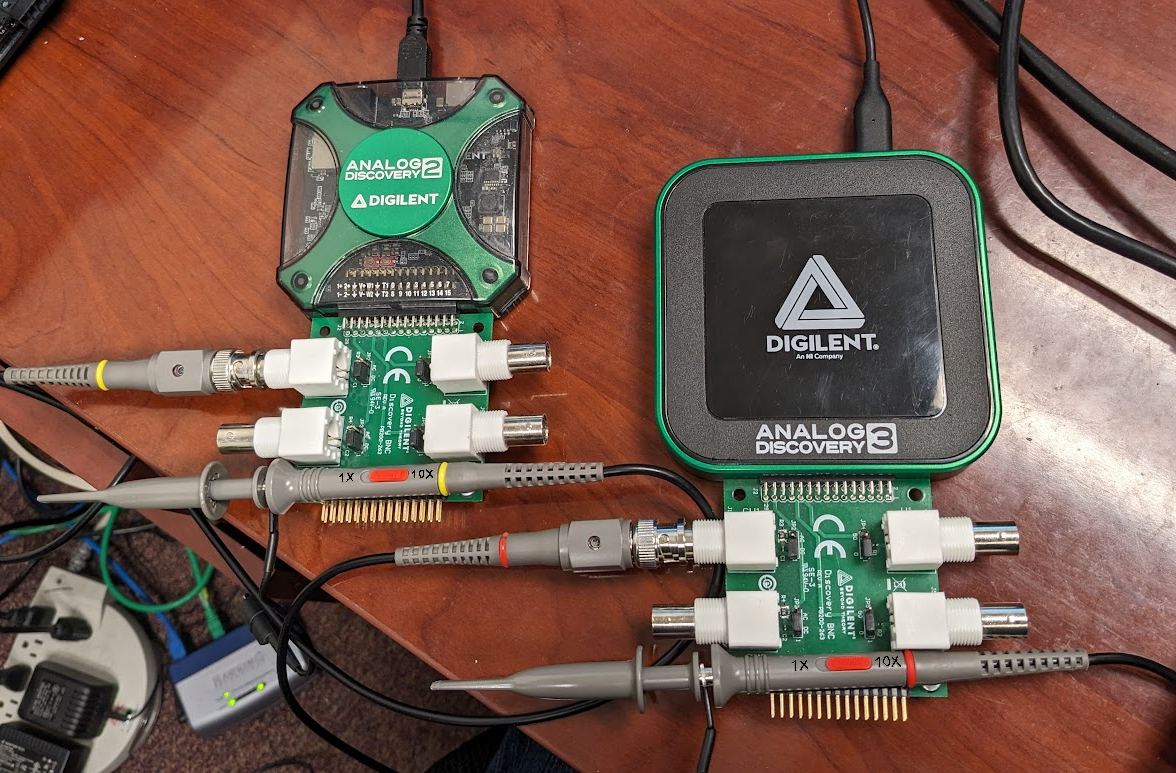
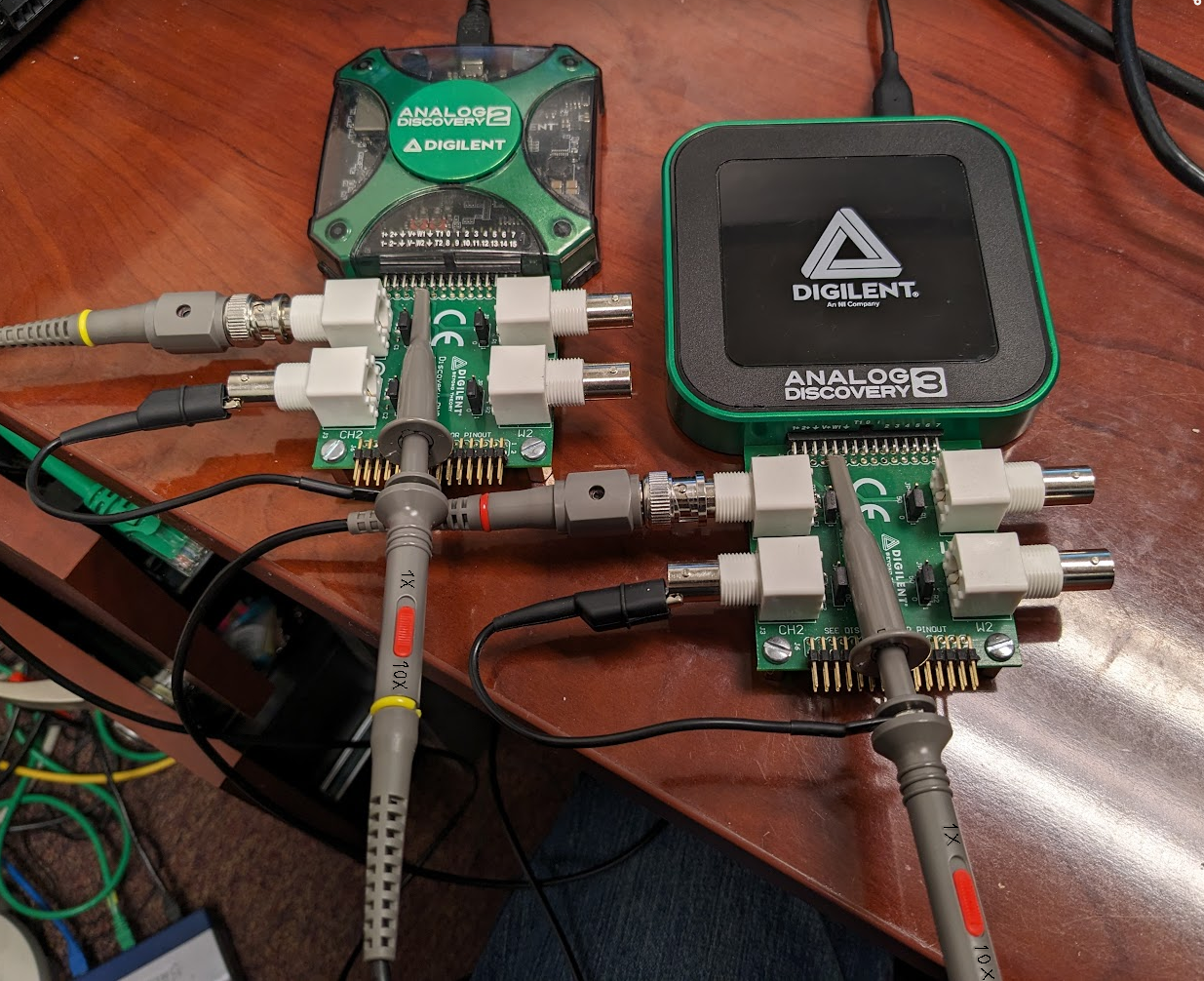
- Analog Discovery 3 or Analog Discovery 2 with BNC Adapter
-
WaveForms Setup
A reference workspace with the recommended setup is available for download in the Inventory. Instructions on how to recreate the workspace for yourself are provided below.
|
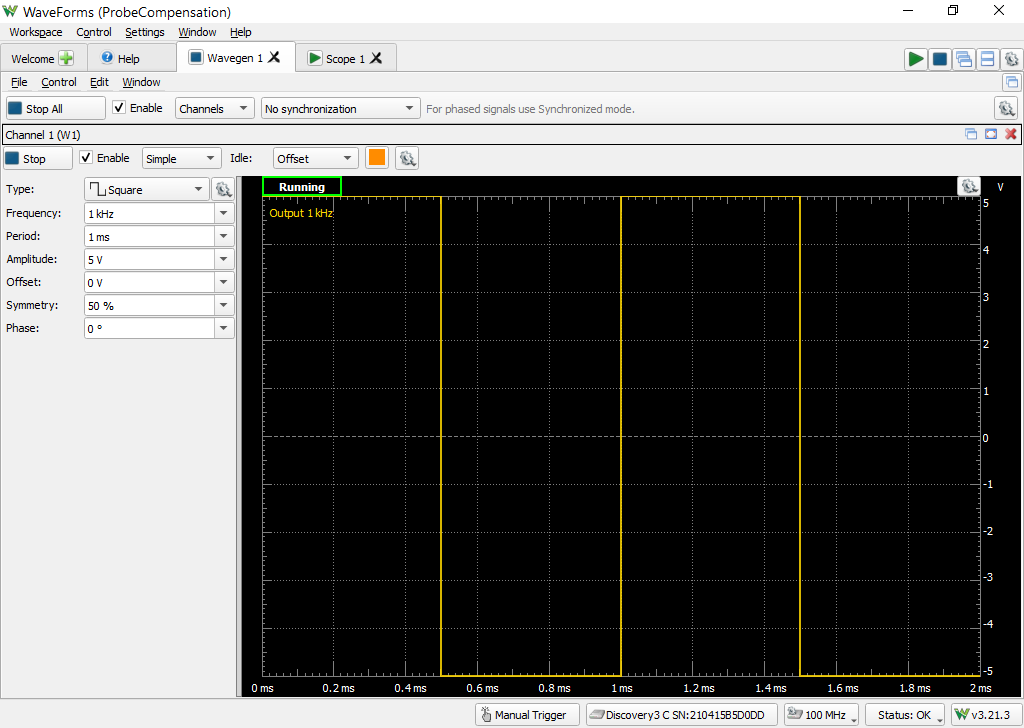
Open the Scope tool in the WaveForms software. Enable the appropriate channel corresponding to what your probe is attached to (likely channel 1) and adjust the following settings:
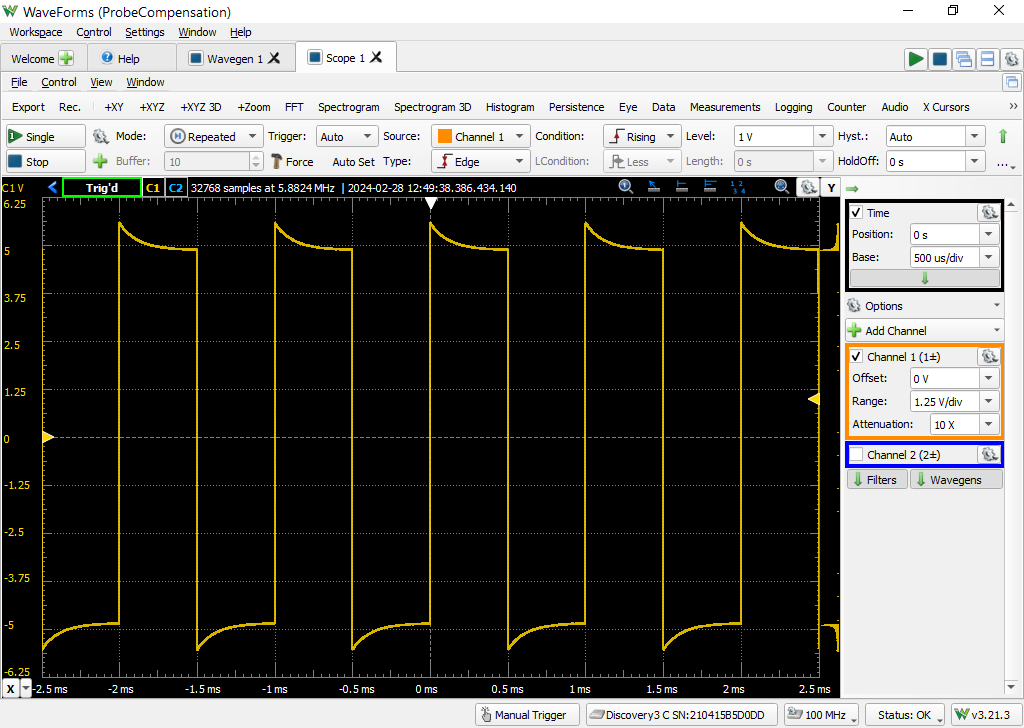
Click the Run All green arrow in the upper right hand corner to start both the Scope and Wavegen instruments. An example of an unattenuated signal that you might see is shown in Figure 29. Note that the provided square wave is in fact not “square” and instead has some overshoot. |
|
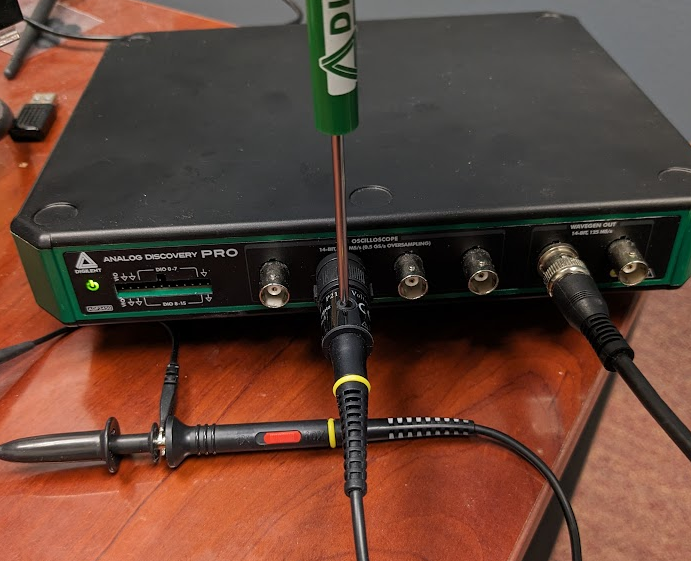
Use a small flathead screwdriver (a small plastic one is typically included with BNC probes) to adjust your probe's compensation capacitor until the square wave visible in the Scope plot looks appropriately square. The probe trimmer is often located on the BNC connector end of the probe as shown in Figure 30.
A small video showing an example of adjusting an overcompensated probe to instead be a flat square wave can be found in Figure 31.

|
|
Next Steps
You have now successfully compensated your BNC probe to a particular oscilloscope channel by adjusting its capacitance to match the capacitance of the oscilloscope channel.
You can find more information about your Mixed-Signal Oscilloscope through its Resource Center, which can be found via the Test and Measurement page of this site.
Other guides you might be interested in include our Calibration guide, the Using External Triggers guide, and Getting Started with WaveForms SDK.
All questions, comments, and observations about this and any of our other guides are welcome on the Test and Measurement section of the Digilent Forum, where Digilent engineers will be able to respond to you directly.