Setting up an Environment for Working with Eclypse and the Zmod Library
This section contains the steps for setting the environment for setting up Baremetal projects and setting up Linux projects for both Zmod Scope and Zmod AWG. Depending on the user's needs, one can either use the projects we deliver in their own development process or use the libraries in their projects. If the second case is considered, the user should apply the described settings below to their project, in order to be able to build it.
Import Library and Demo Projects
The steps below need to be followed in order to obtain a complete SDK workspace and to be able to build and run any of the projects, in either Linux or Baremetal platforms.
Linux Environment Project Setup
The ZmodADC1410_Demo_Linux and ZmodDAC1411_Demo_Linux are run from Xilinx SDK.
This step-by-step tutorial roughly follows the How to debug Linux Application in SDK 2019.1 by Xilinx, with some changes due to our Debian 10 rootfs.
The following steps are for the Eclypse Z7 board. If a Zmod Scope is used, it should be attached to the Eclypse Z7's ZMOD A port. If a Zmod AWG is used, it should be attached to the Eclypse Z7's ZMOD B port.
1. Download the Source Code
- Download the git repository containing the libraries and demos using the below command:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/Digilent/Eclypse-Z7-SW.git -b zmod_adc_dac/master
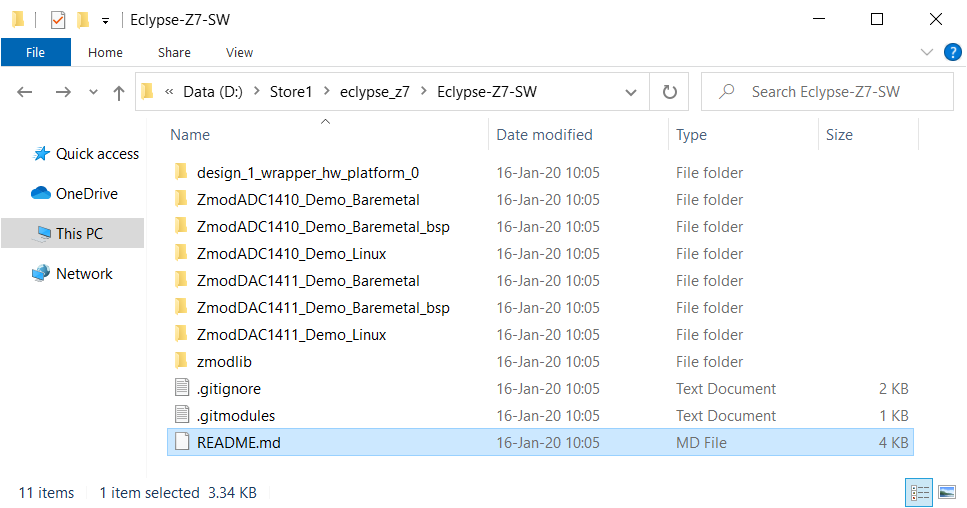
The directory created when you run this command (“Eclypse-Z7-SW”), will be used as the Xilinx SDK workspace in later steps.
Note: If you choose to download the repository as ZIP, the folder zmodlib will not be populated and you will have to populate it manually.
If you want to download the Vivado and PetaLinux projects at the same time, instead clone the Eclypse-Z7 repository (still using the zmod_adc_dac/master branch). Instructions on working with these projects, as well as on how to check them out from source, can be found in the Eclypse Z7 Git Repositories documentation.
2. Download the SD Card Image
- Download the latest eclypse-debian-buster-armhf-rfs.img_X.X.zip Petalinux image from the Eclypse Z7 git repository Releases and extract it on your PC.
- You need to expand the Assets section to see the files.
- Write the image to an SD card:
- Linux: in a terminal window use the following command:
dd if=/path/to/extracted/image/eclypse-debian-buster-armhf-rfs.img of=/dev/(sdX or mmcblkX} && sync
- Windows: use Rufus or Win32DiskImager.
- Connect the board to your Ethernet network.
- Insert the SD card and boot the board. On first boot, the rootfs partition will resize to fill the SD card then reboot.
- Open a Terminal and connect to the board via its USB-UART interface (labeled PROG) with a baud rate of 115200.
- Login with username: eclypse and password: eclypse.
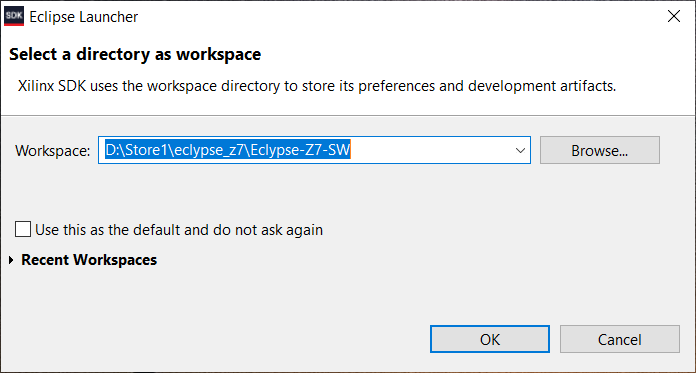
3. Select Xilinx SDK Workspace Location
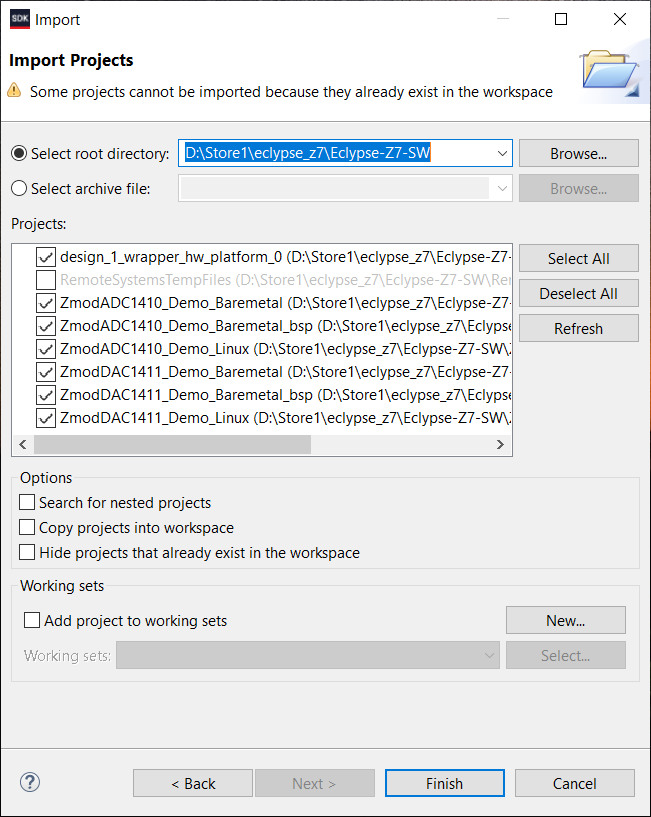
- The downloaded workspace contains demo applications for both Linux and Baremetal and is intended to be used in place.
- Open Xilinx SDK 2019.1 and assign the workspace location to the project download location.
- If you want to use the demo projects, open the desired Linux or Baremetal demo project. The projects are already configured and ready to be used, except the Linux project where SYSROOT environment variable must be set according to the Add SYSROOT Environment Variable section (step 1.5, below).
5. Add SYSROOT Environment Variable in SDK
- Download the latest eclypse-debian-buster-armhf-sysroot_X.X.tar.xz (.zip for Windows ) sysroot from the Eclypse Z7 git repository's Releases page and extract it on your PC (the location of the extracted folder will be later used as the path for the SYSROOT Environment Variable)
Note: You need to expand the Assets section from github to see the eclypse-debian-buster-armhf-sysroot_X.X.tar.xz and .zip files.
Windows only: When prompted whether to replace existing files, choose to replace. - In the SDK Project Explorer, right-click on the application project you wish to run, then click “C/C++ Build Settings”
- In the “C/C++ Build” group, select the “Environment” category
- Add the SYSROOT variable pointing to the location where eclypse-debian-buster-armhf-sysroot rootfs folder can be found. For example “/home/cosmin/Documents/eclypse-debian-buster-armhf-sysroot”
Windows: The SYSROOT environment variable if exists must be Deleted then reAdded to the list, rather than Editing the existing variable. - Click OK and wait for the Project to build
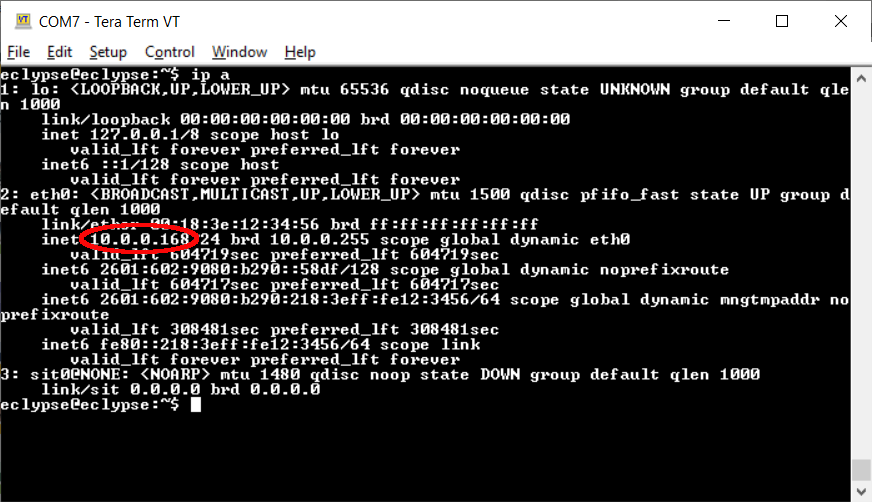
6. Find the Board IP Address
- In the UART Terminal connected to the board, log in with the username/password combination eclypse/eclypse
- Run the following command:
ip a
- Copy the IP address of the board, example: 10.0.0.168
7. Establishing Connection to the Board
- In the SDK Target Connections panel, open the Linux TCF Agent folder
- Right-click on Linux Agent [default] and click Edit
- Enter the board IP address into the Host section
- Click Test Connection to make sure that SDK can communicate with the TCF-agent on the board
- Click OK
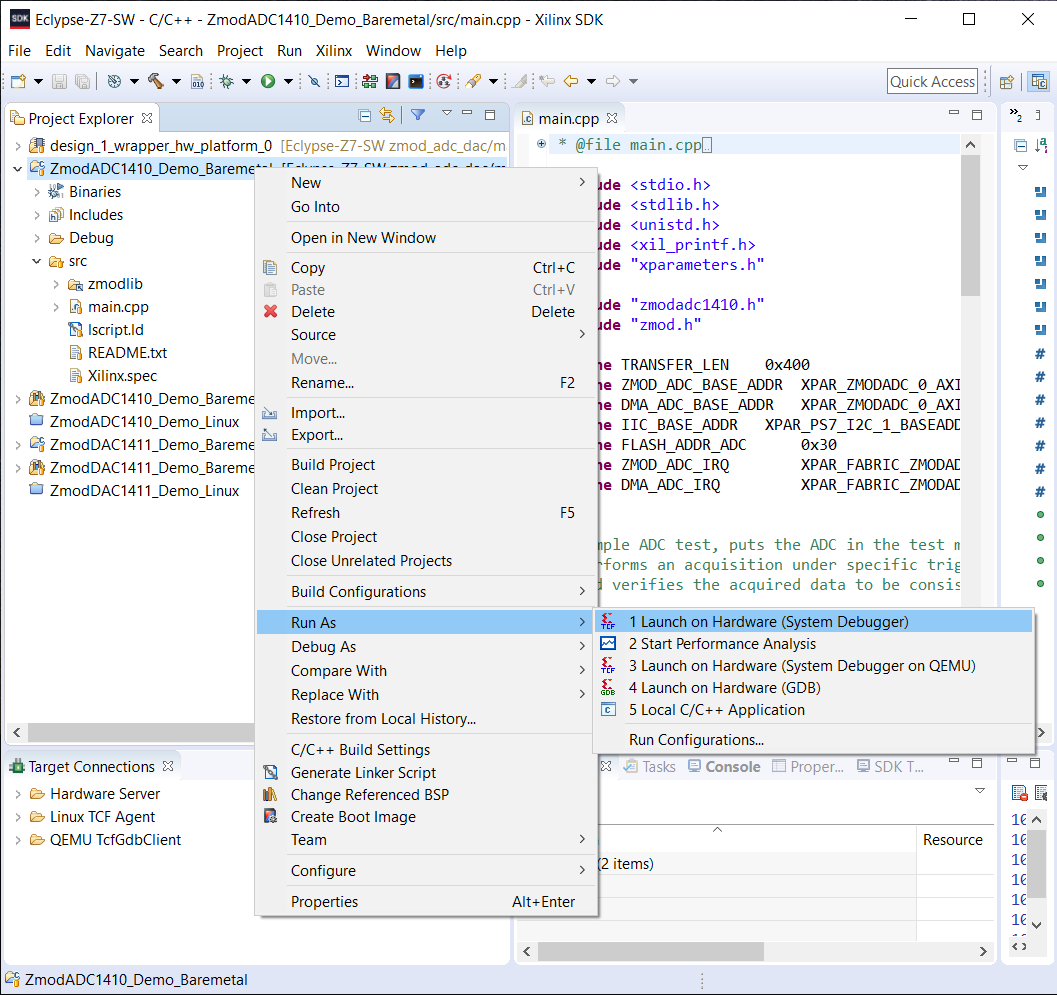
8. Run the Demo Project
To run the demo application, right-click on Project name → Run as → Launch on Hardware(System Debugger)
Baremetal Project Setup
1. Download the Source Code
Download the demo project with the below command:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/Digilent/Eclypse-Z7-SW.git -b zmod_adc_dac/master
The directory created when you run this command (“Eclypse-Z7-SW”), will be used as the Xilinx SDK workspace in later steps.
Note: If you choose to download the repository as ZIP, the folder zmodlib will not be populated and you will have to populate it manually.
If you want to download the Vivado and PetaLinux projects at the same time, instead clone the Eclypse-Z7 repository (still using the zmod_adc_dac/master branch). Instructions on working with these projects, as well as on how to check them out from source, can be found in the Eclypse Z7 Git Repositories documentation.
2. Add Xilinx SDK Workspace Location
- The downloaded workspace contains demo applications for both Linux and Baremetal.
- Open Xilinx SDK 2019.1 and assign the workspace location to the project download location.
- If you want to use the demo projects, open the desired Baremetal demo project. The projects are already configured and ready to be used.
4. Xilinx SDK Project Explorer
- The ZmodADC1410_Demo_Linux and ZmodDAC1411_Demo_Linux projects must be closed or deleted from Project Explorer (right-click on project name→ Close Project or Delete)
5. Run the Demo Project
- Make sure the board is connected to your PC and it is powered on.
- If required by the particular demo application, connect a serial terminal application to the device's port, using a baud rate of 115200.
- Make sure the jumpers are set accordingly.
- Program the board: Xilinx → Program FPGA
- Run the demo application: right-click on project name → Run as → Launch on Hardware(System Debugger)