This is an old revision of the document!
Using Digilent Github Demo Projects
Overview
Digilent provides several projects through Github that are designed to demonstrate different uses of our FPGA and Zynq boards. This guide will describe how to download and use these projects.
At the end of this tutorial you will have your demo project running on your board.
Prerequisites
Hardware
- A Supported Digilent 7-Series FPGA or Zynq Board
- USB Cables
Software
- Xilinx Vivado 2016.X
- Vivado 2016.4 is used in this tutorial
- Digilent Board Support Files
- Follow the wiki guide on how to install Board Support Files for Vivado 2016.X
- Projects Supported by this Tutorial
-
Platform Project Name Uses SDK Hardware Handoff Available Wiki Link Github Link Arty Pmod VGA Demo No No Internal Link External Link Zybo DMA Demo Yes Yes Internal Link External Link
Important
For further requirements, please review the project's wiki page.
Tutorial
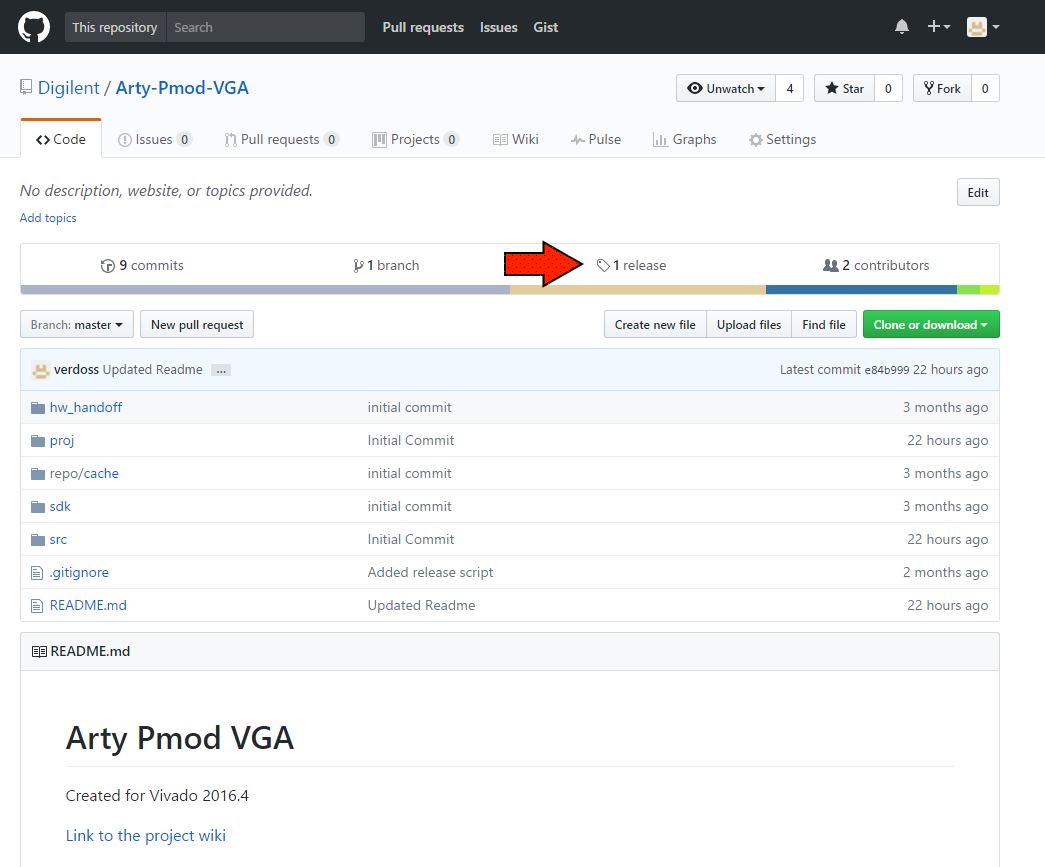
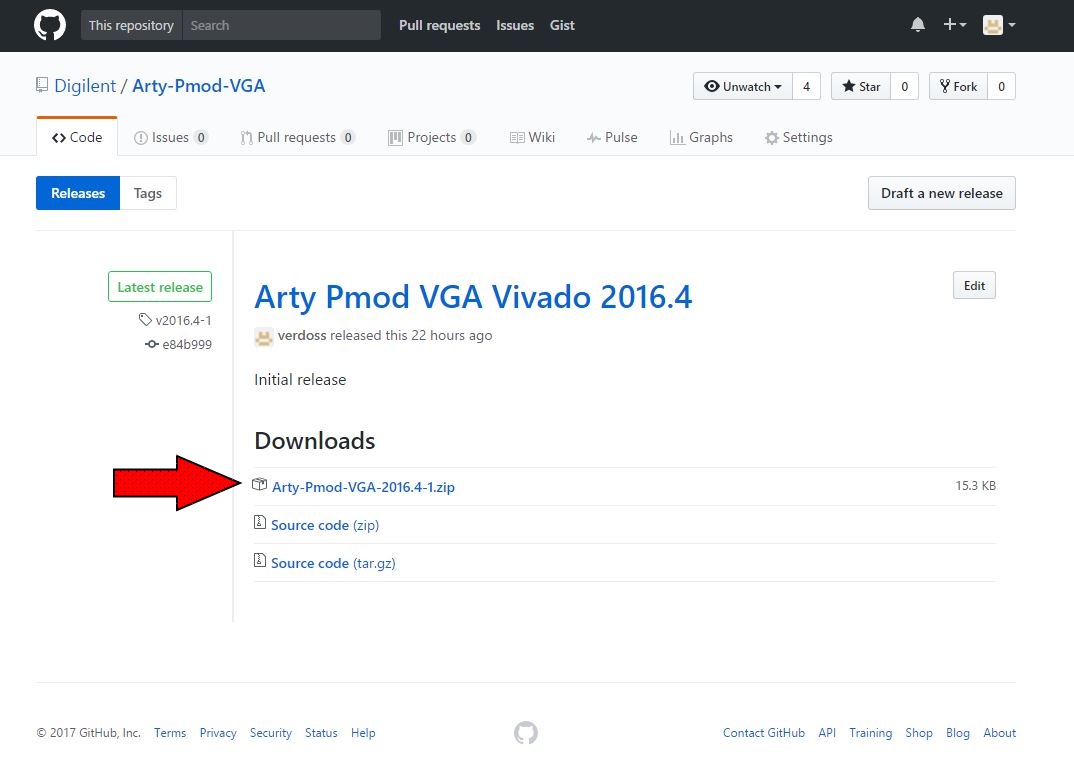
1. Download the Project ZIP from the Digilent Github
1.3) All of the necessary files are included within each project folder, with relative file paths established, so as long as the files aren't moved around within the folder, you can move and run the project from any location.
2. Open the Project
Select the “SDK Hardware Handoff” option if your project supports Vivado SDK and you want to jump directly in, otherwise select the “Vivado” option. Review the Supported Projects table above to determine if the Hardware Handoff option is available.
- SDK Hardware Handoff
-
2.1) Find and Launch Vivado SDK. This till open a “Select Workspace” dialog. Click Browse, then find and select the “sdk” directory of your project.2.2) Click Ok to finish launching SDK.
- Vivado
-
2.2) Open Vivado and find the Tcl Console on the bottom of the window. Enter the letters 'cd' (change directory) followed by the file path you copied earlier. Select the proj folder from the drop down menu to make sure that Vivado converts the path's back slashes ' / ' to forward slashes ' \ '.
Important
Vivado will not recognize paths that include back slashes, be very careful to make sure that it is properly converted.
3. Generate Bitstream
Skip this step if you previously selected the SDK Hardware Handoff option.
- Generate Bitstream
-
3.1) Click Generate Bitstream on the left hand menu towards the bottom. In the “Launch Runs” dialog, make sure Launch runs on local host is selected and click OK. In the “No Implementation Results Available” dialog, click Yes to run synthesis and implementation.
Tip
If your computer has multiple CPU cores, you can increase the number of jobs to make this process faster.
3.2) When this process has finished, which may take a while, in the “Bitstream Generation Completed” dialog you will be presented with several option. You can Open Implemented Design to view how your design will be placed onto the FPGA. View Reports will show you a number of different diagnostics on your project, including how the resources of your board will be used. Open Hardware Manager is used to program the bitstream onto the board (this will not be used for the SDK flow). Generate Memory Configuration File creates a file that can be used to program the bitstream from local memory on your device.
4. Import SDK Projects
Skip this step if your project doesn't support SDK.
- SDK Hardware Handoff
-
4.1) In SDK's main page, click the Import Projects button.4.2) If it is not checked, check the Select root directory option. Click Browse, again find and select the “sdk” directory.4.3) Make sure that the hw_handoff, application, and application board support package (BSP) projects are all checked, then click Finish to open the projects in SDK.
- Launch from Vivado
-
4.1) If the “Generate Bitstream Complete” dialog is still open, click Cancel.4.2) In the top toolbar, select File → Export → Export Hardware.4.3) Make sure that the “Include bitstream” checkbox is checked and that the hardware platform will be exported to <Local to Project>. Click Ok.4.4) In the top toolbar, select File → Launch SDK, make sure that “Exported location” and “Workspace” are set to <Local to Project>. Click Ok.4.5) In SDK, from the top toolbar, select File → Import.4.6) In the “Select an import source” dialog dropdowns, select General → Existing projects into workspace, then click Next.4.7) In the “Import Projects” dialog, click Browse next to “select root directory”, then find and select the sdk subdirectory of your project. Click Ok.4.8) Make sure that the application and application board support package (BSP) projects are checked, then click Finish.
Tip
Many apparent errors at this stage can be solved by right-clicking the bsp project and selecting Re-generate BSP Sources.
5. Run the Project
If you have opened your project in SDK in previous steps, select the “SDK” option, otherwise, select “Vivado”.
- SDK
-
5.1) Ensure your board is turned on and connected to your computer by a JTAG-USB cable.5.2) Revisit the project's wiki page to check for extra requirements, such as setting up a serial terminal, or connecting additional cables.5.3) Select Program FPGA from the Xilinx Tools dropdown in the toolbar. Then click Program.5.4) Right click on the application project - the one that doesn't end with “_hw_platform” or “_bsp” - and under “Run As”, select Launch on Hardware (System Debugger).5.5) The project will now be programmed and running on your board and you can return to the project's wiki page to verify functionality.
- Vivado
-
5.1) In the Generate Bitstream Complete dialog, select “Open Hardware Manager”, then click Ok. If the dialog is no longer open, select Hardware Manager from the Program and Debug section of the Flow Navigator to the left, just underneath Generate Bitstream.5.2) Ensure your board is turned on and connected to your computer by a JTAG-USB cable.5.3) Revisit the project's wiki page to check for extra requirements, such as setting up a serial terminal, or connecting additional cables.5.4) Select Open Target from the green bar at the top. In the drop down menu that this creates, select Open New Target.5.5) Click Next. Then make sure that Local server is selected in the “Connect to” drop down. Connect your board to your computer with a JTAG USB cable, then click Next.5.6) Select Program Device from the green bar, then select your device from the dropdown list (there will usually only be one device listed). Then click Program.
Important
If nothing shows up in the “Bitstream file” text box, click the … button to the right, navigate to “proj/*.runs/impl_1” subdirectory of your project and select the “*.bit” file.
5.7) The project will now be programmed and running on your board and you can return to the project's wiki page to verify functionality.