Recently the Xcell blog published a helpful article on the different uses of SPI, specifically regarding the use of SPI with the Zynq SoC and Zyincq UltraScale+ MPSoC.
The author outlines the specific design choices one must make when using a Zynq SoC or Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC, as well as step-by-step examples on getting up and running with an Arty Z7 used in the example. He provides troubleshooting along the way which pertains both the the specific design he is using as well as common problems users may face when working with SPI.

The author demonstrates his design by connecting the SPI master example to a Digital Discovery to capture transmitted data. He then changes the data width on the fly from 8 to 16 bits using methods in the software. He outlines these methods so users can follow his steps and do try it out themselves!
Additionally the article details when one would want to use these methods and relevant alternatives.
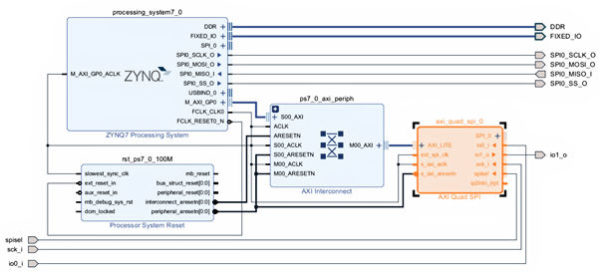
The alternative to implementing a SPI interface using the Zynq PS is to implement an AXI QSPI IP core within the Zynq PS. Doing this requires more options being set in the Vivado design, which will limit run-time flexibility.
After implementing the AXI QSPI core as a SPI Slave, he used the Digital Discovery again to act as the SPI Master, allowing data to be easily transferred. His final design was created in Vivado for both examples, and is currently uploaded to github.
If this material is of relevancy to you or your projects, make sure to head over to Xcell and check out the full article!


Hello,
Have you tried the same thing on Zynq Ultrascale+?
Cheers,