Pmod HB5 Reference Manual
The Pmod HB5 is retired and no longer for sale in our store.
The Digilent Pmod HB5 (Revision E) offers a 2A H-bridge circuit to drive small to medium sized DC motors. This module was specifically designed to work with the Digilent gearbox motor which incorporates quadrature encoder feedback.
Download This Reference Manual
Features
- 2A H-bridge circuit
- Drive a DC motor with operating voltage up to 12V
- 6-pin JST connector for direct connection to Digilent motor/gearboxes
- Two screw terminals for external motor power supply
- 6-pin Pmod port with GPIO interface
Functional Description
The Pmod HB5 utilizes a full H-Bridge circuit to allow users to drive DC motors from the system board. Two sensor feedback pins are incorporated into the motor connection header and are specifically designed to work with the Digilent motor/gearbox (1:19 gear ratio) Digilent motor/gearbox (1:53 gear ratio).
Interfacing with the Pmod
The Pmod HB5 communicates with the host board via the GPIO protocol. Like all H-Bridges, care must be taken to avoid causing a potential short within the circuitry. In terms of this Pmod, this means that the Direction pin must not change state while the Enable pin is at a high voltage state. If this does occur, one set of switches that are driving the motor will be closing while the other set is opening, allowing for the possibility for both sets of switches to be open at the same time, creating a short.
To drive the motor at a specific speed, users will need to choose a static direction (provide a low voltage to the Direction pin to rotate the shaft in a clockwise direction or provide a high voltage on the Direction pin to rotate the shaft in a counter-clockwise direction) on the Direction pin, and then perform pulse width modulation on the Enable pin. The more often that the Enable pin is driven high within a set time frame, the faster the DC motor will spin.
The way that this works is that when voltage is being applied, the motor is driven by the changing magnetic forces. When voltage is stopped, momentum causes the motor to continue spinning a while. At a high enough frequency, this process of powering and coasting enables the motor to achieve a smooth rotation that can easily be controlled through digital logic. 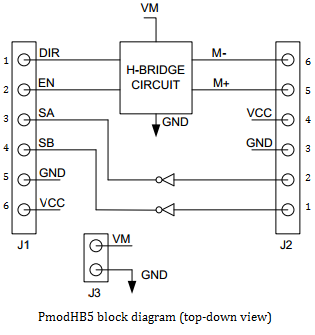
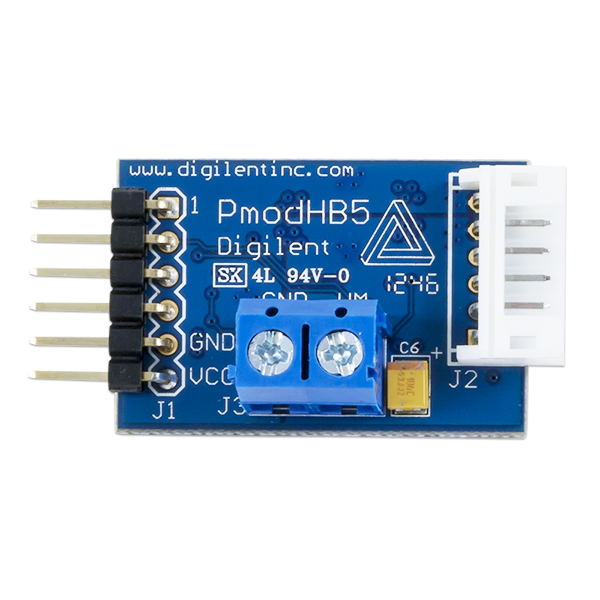
Pinout Description Table
| Header J1 (pin 1 on the top) | Header J2 (pin 1 on the bottom) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin | Signal | Description | Pin | Signal | Description | |
| 1 | DIR | Direction pin | 1 | SB | Sensor B feedback pin | |
| 2 | EN | Enable pin | 2 | SA | Sensor A feedback pin | |
| 3 | SA | Sensor A feedback pin | 3 | GND | Power Supply Ground | |
| 4 | SB | Sensor B feedback pin | 4 | VCC | Positive Power Supply (3.3/5V) | |
| 5 | GND | Power Supply Ground | 5 | M+ | Motor positive pin | |
| 6 | VCC | Positive Power Supply (3.3/5V) | 6 | M- | Motor negative pin | |
Any external power applied to the Pmod HB5 must be within 2.7V and 5.25V; however, it is recommended that Pmod is operated at 3.3V.
Physical Dimensions
The pins on the pin header are spaced 100 mil apart. The PCB is 1.2 inches long on the sides parallel to the pins on the pin header and 0.8 inches long on the sides perpendicular to the pin header.
Additional Information
The schematics of the Pmod HB5 are available here.
Example code demonstrating how to drive and receive sensor feedback from the Pmod HB5 can be found here.
If you have any questions or comments about the Pmod HB5, feel free to post them under the appropriate section (“Add-on Boards”) of the Digilent Forum.