Genesys 2 - Programming Guide
Overview
There are four ways you can program the Genesys2:
- JTAG
- Quad SPI Flash
- USB Flash Drive
- Micro SD Card
This tutorial will walk you through what you need to know to get started on your projects and program your Genesys2 FPGA board using each of the three possible methods. It is recommended that you first complete the “Getting Started with Vivado” guide before continuing with this project. NOTE: The Genesys2 requires Vivado Design Edition or System Edition which supports the Kintex-7 FPGA. This is not the same as the free webpack version.
Prerequisites
Skills
- Basic familiarity with Vivado
- This experience can be found by walking through our “Getting Started with Vivado” guide
Hardware
- Genesys2 FPGA board
- Micro-USB cable
- Micro SD card
Software
- Vivado Design Suite 2015.X
- System Edition or Design Edition must be installed to support Kintex-7
Board Support Files
- Genesys2 Support Files
- These files will describe GPIO interfaces on your board and make it easier to select your FPGA board and add GPIO IP blocks.
- Follow the Wiki guide: Vivado Board Files for Digilent 7-Series FPGA Boards on how to install Board Support Files for Vivado.
Downloads
Source Files – ZIP
Tutorial
1. Creating the Project
First we will need to create a project.
1.1) Open up Vivado and click Create New Project to open Vivado's New Project wizard.
1.2) A new window will open up, click Next and you'll see the screen below. Name your project (no spaces!) and choose your project saving directory before clicking Next.
1.3) We will be building this project from the ground up and adding our own sources so we will want to create an RTL project. select RTL Project and click Next.
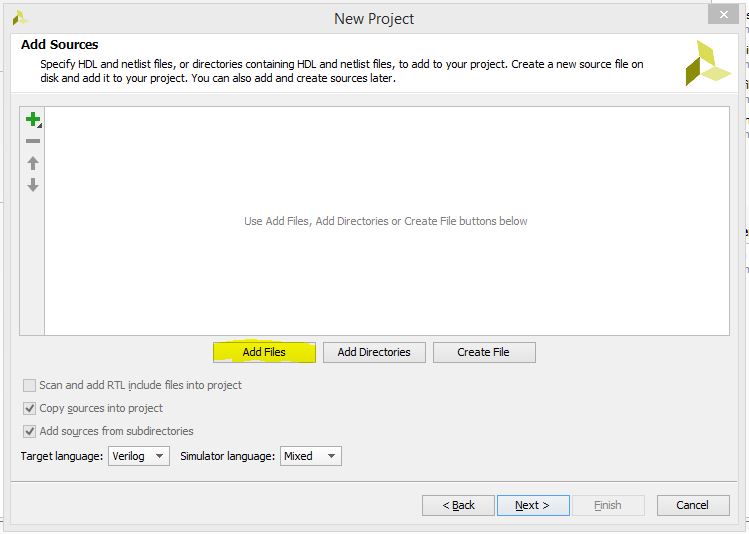
1.4) In this window, you can select any source files or directories that you'll want to use in your projects. We can also select which language we'll be programming in. For this project just keep the default settings. Create a new file by clicking the Create File button.
1.5) Find sw_led.v within the source files folder you downloaded and click Ok. The Copy sources into project checkbox will be enabled by default. This creates another sw_led.v within our project directory so that the original will not be altered. Click Next to continue.
1.6) This window lets you choose existing IP (Intellectual Property) cores if you have them, but for this tutorial no IP's will be necessary. Click Next.
1.7) This is where we'll import our Xilinx Design Constraints file (XDC) to map the HDL signals to the Kintix-7 pins. Click Add Files, navigate to where you saved your Genesys2_H.xdc file, select it, and click Next.
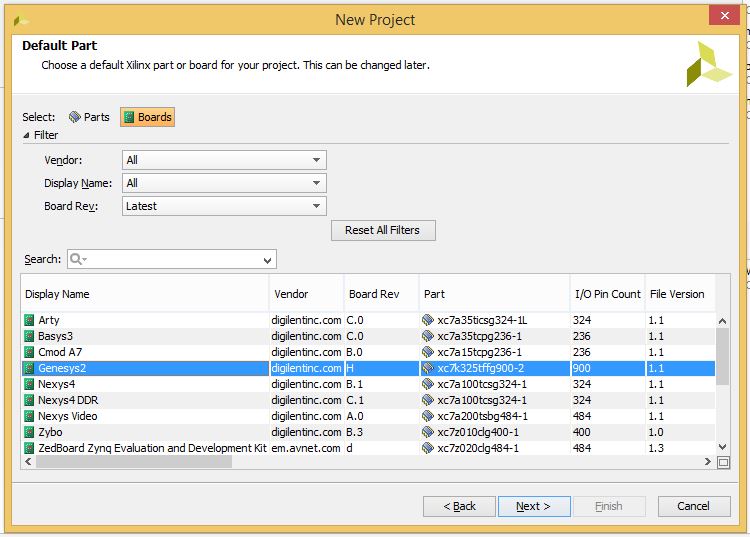
1.8) At this point Vivado will open up a part selection window. Select the Boards tab highlighted in orange below. If you installed the board files correctly, you should see a list of Digilent boards. Select the Genesys2 and click Next.
This will create your project and bring you to the Vivado project manager.
You have now successfully created/imported your program files and configured your project to properly communicate with the Genesys2.
2. Creating Program File
For the four ways to program your Genesys2 FPGA there are two file types available; .bit and .bin files. Using a .bit file we can use either the JTAG programming cable, or a standard USB storage device to load the bit file into the FPGA. Programming with a .bin file will use the QuadSPI to program the FPGA each time it is powered on. This means you will not have to reprogram it each time via a micro USB cable or by a thumb drive. The following steps bellow will get you all prepared to program your Genesys2.
2.1) In order to program the FPGA on startup we have to specify that we want to generate a .bin file. This can be done by clicking Tools→Project Settings→Bitstream. In this window we will check the box next to .bin_file. Now Vivado will create both a .bit, and .bin file when we generate a Bitstream.
2.2) To begin, we will run the synthesis by clicking Run Synthesis beneath Synthesis in the Flow Navigator on the left side of Vivado.
2.3) When the program finishes synthesizing your project, you will see the Synthesis Completed window below. Click Open Synthesized Design and then press Ok.
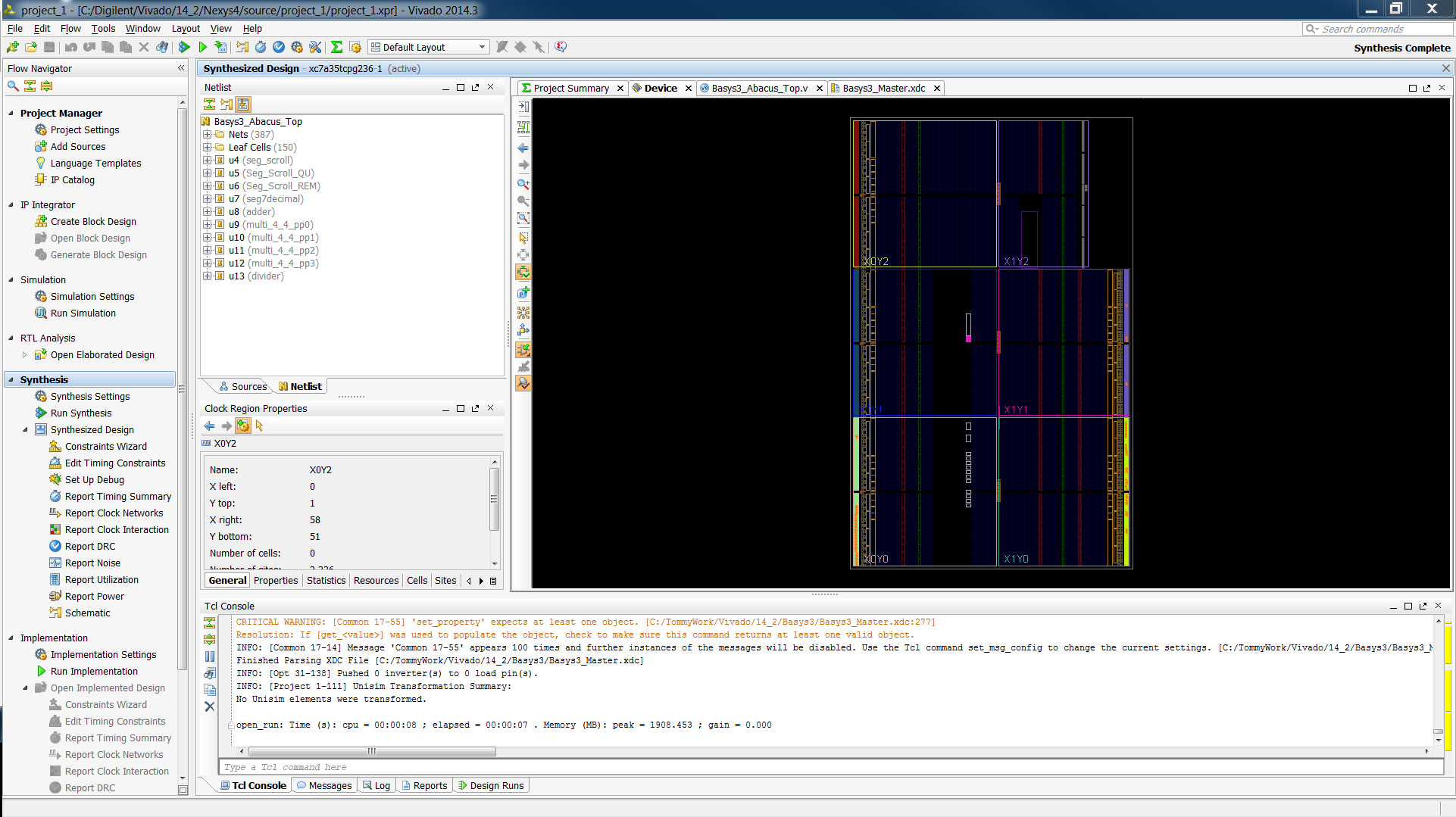
2.4) You should now see your Synthesized Design in the window to the right. It should look like this:
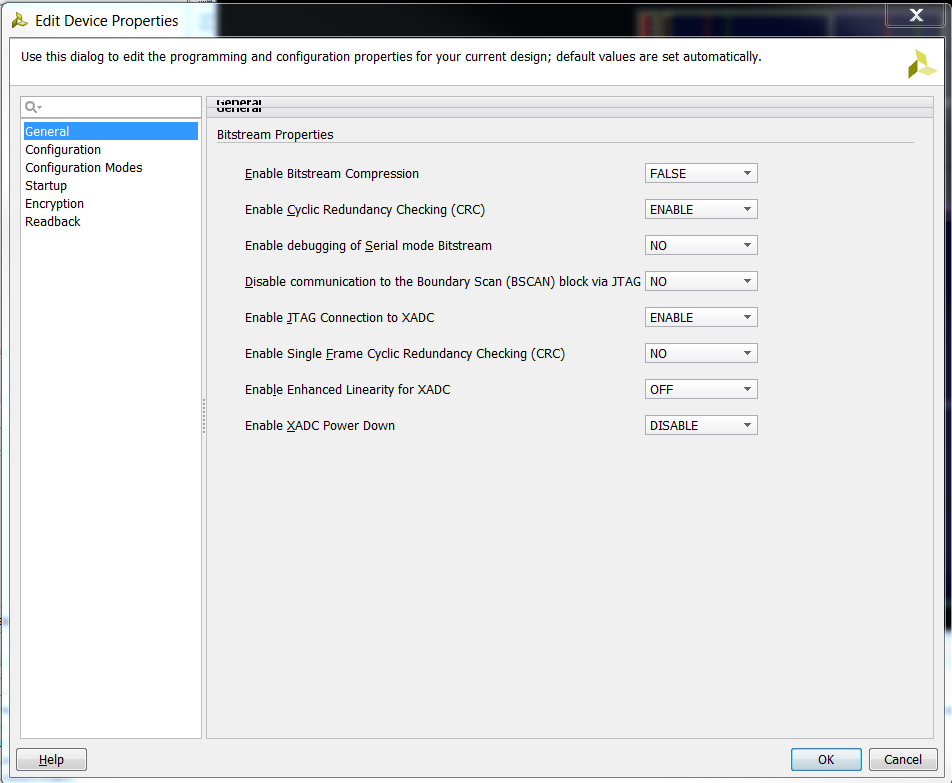
2.5) To improve programming speed of our .bin file, in the main toolbar select Tools→Edit Device Properties. Under General, set Enable Bitsream Compression to “TRUE”.
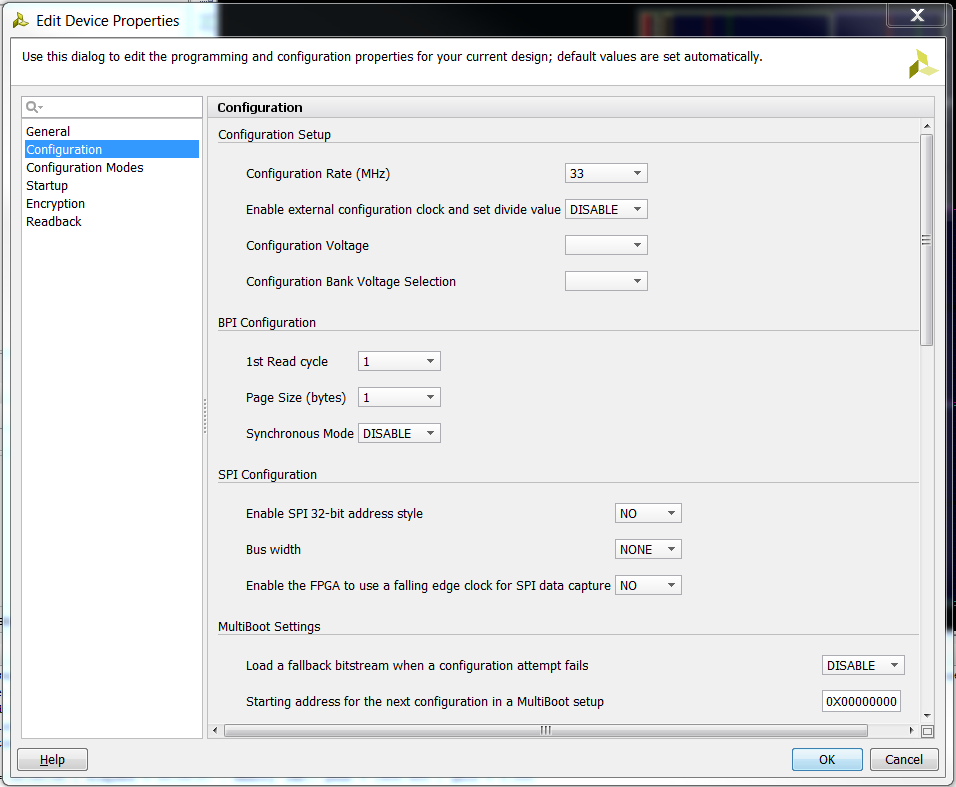
2.6) Under Configuration, set Configuration Rate (Mhz) to 33.
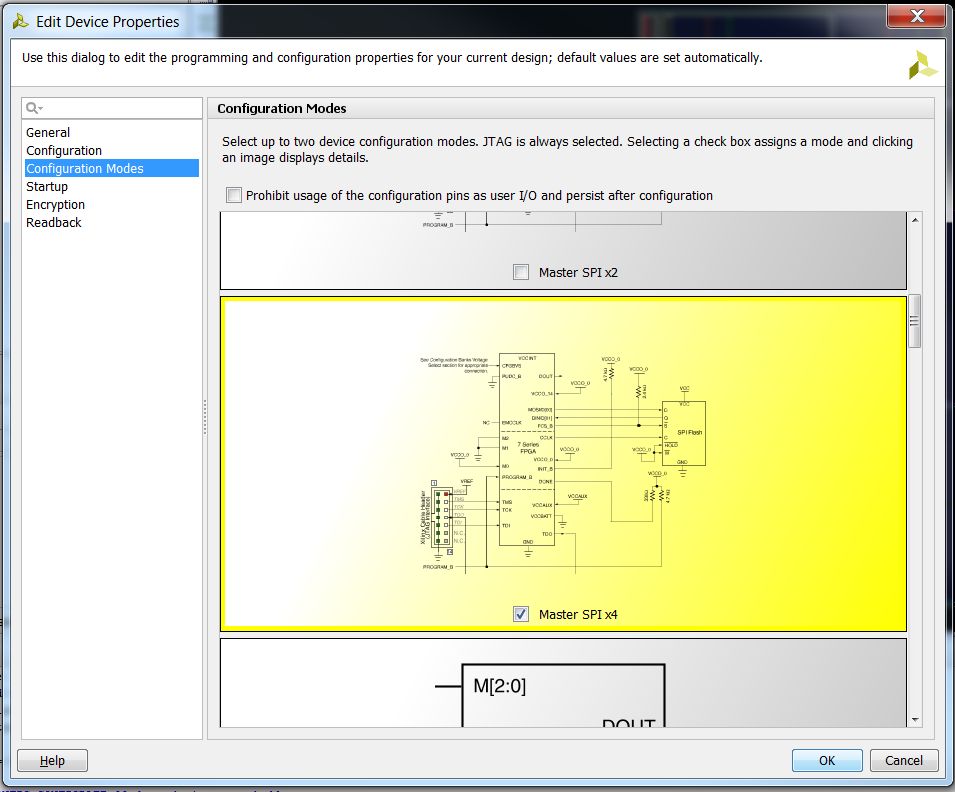
2.7) Under Configuration Modes, select Master SPI x4.
2.8) Click Ok, save your synthesized design (Ctrl+S) and then click Generate Bitstream in the Flow Navigator on the left side.
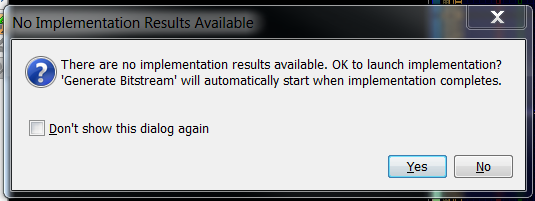
2.9) This will open a box stating that you have not implemented your design. Click Ok.
2.10) Vivado will begin generating your bit and bin files. When completed Vivado will show you this box. Feel free to select Open Implemented Design, or View Reports but you can also just Cancel to continue with the guide.
At this point you have successfully created a .bit and .bin file that are ready to program the Genesys2. As said previously there are four ways to program the Genesys2 FPGA board, and we will be walking through each one of them below.
3. Programming the Genesys2 using JTAG
JTAG is primarily used as a programming, debugging, and probing port and communicates through the micro-USB port. This makes interfacing with the Genesys2 easy because the micro-USB connection both supplies power to your board, and the ability to program it.
3.1) First, make sure that the jumper JP5 is in the JTAG position and that the Genesys2 is plugged into your computer via micro-USB cord into the JTAG port. Once the board is plugged in you should see something like this.
3.2) Click Program device (in the green bar), then click xc7k325t_0, and select your .bit file in the bitstream file box, and click Program.
This will program your Genesys2 through the JTAG connector. Once the programming window is closed go ahead and test out your board. Each slide switch at the bottom of your board should now toggle its respective LED on and off.
4. Programming the Genesys2 using a USB Flash drive or SD card
It is important to note that the USB device that you select to program the Genesys2 must be formatted in Fat32. Other than that your device doesn't have to be empty and can contain other files and folders. At this point Vivado is no longer needed to program the FPGA, so you can minimize your project and follow these steps in File Explorer:
4.1) Make sure the jumper on JP5 is in the USB/SD position and that JP4 is in the USB position if using a USB drive, or SD if using an SD Card.
4.2) Plug your USB flash device or SD Card into your computer.
4.3) Open File Explorer and navigate to the root folder of your Vivado project.
4.4) From root go to root→Project_name.runs→impl_1 and copy the .bit file.
4.5) Go to the root of your USB device and paste the .bit file. The Genesys2 on startup will only look through the USB's root for a file with a .bit extension so it is important that the only .bit file in root is the one that you want to be used to program the Genesys2.
4.6) Safely remove the device from your computer and plug it into the Genesys2.
4.7) Make sure your board is connected to your computer for power and turn on the Genesys2. It should immediately begin writing the .bit file to the FPGA.
Once finished your board should function exactly as it did when programming it with JTAG. Whether you were aware or not you just successfully programmed your Nexsys 3 board two separate ways using the same .bit file.
5. Programming the Genesys2 using Quad SPI
Quad SPI Flash is a non-volatile memory that the Genesys2's FPGA chip looks at on every startup. If Quad SPI is flashed then the FPGA will program itself with the contents found in Quad SPI's flash memory. This method of programming your board is great when you have a final project that you would like to demo or display that doesn't need to be edited and therefore reprogrammed.
5.1) Make sure the jumper on JP5 is in the QSPI position
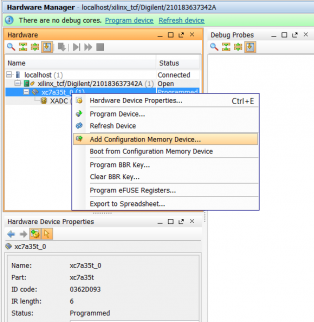
5.2) In the Hardware Manager window, under hardware right click your device and click Add Configuration Memory Device…
5.3) This window will pop up. Search for “Spansion” and select s25fl256sxxxxxx0-spi-x1_x2_x4. Click OK on the next window asking if you want to program the configuration memory device.
5.4) Select the .bin file (found in your project/project.runs/impl_1/ folder) where it asks for a configuration file and finally click OK.
Vivado will now erase the old configuration file, and reprogram your Genesys2 with the demo file. From now on, when you power up the Genesys2, the demo will load at startup until you reprogram it.