Motor Shield Reference Manual
Note
The Motor Shield is retired and no longer for sale in our store.
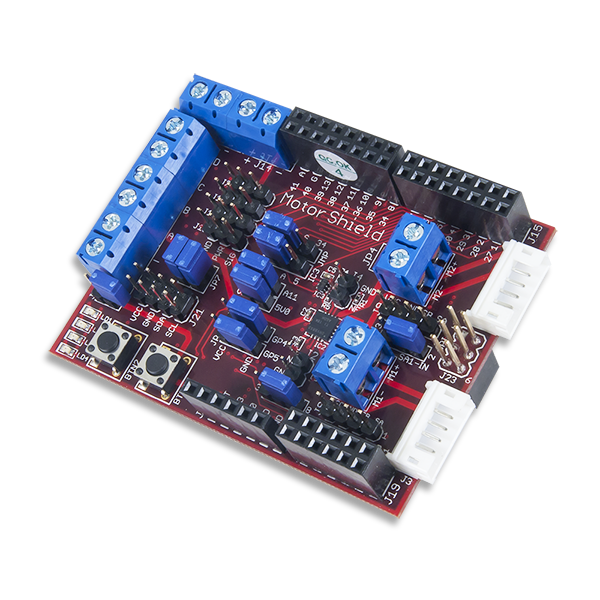
The Motor Shield is an expansion board for use with the Uno32 and uC32. It provides additional circuitry and connectors for the Uno32 and uC32 to drive various motors types.
The Motor Shield is designed to drive DC motors, servo motors, and stepper motors. It also provides additional I/O via an I2C I/O extender.
Features include
- Two DC motor driver channels, accessible with either a JST 6-pin connector or a terminal block
- Two DC motor encoder input signals for each DC motor channel
- Four servo motor channels
- I2C General purpose I/O expander with 4 LEDs 2 push buttons and 2 user settable jumpers
- One 4-wire unipolar stepper motor channel
- Standard Shield connectors
1. Functional Description
The Motor Shield is designed to be used with the Uno32 or uC32 board. When used with these boards, the microcontroller and shield provide the necessary supporting hardware and connectors to control most types of small motors. The rest of this document will only reference the Uno32; however, the shield can also be used with the uC32.
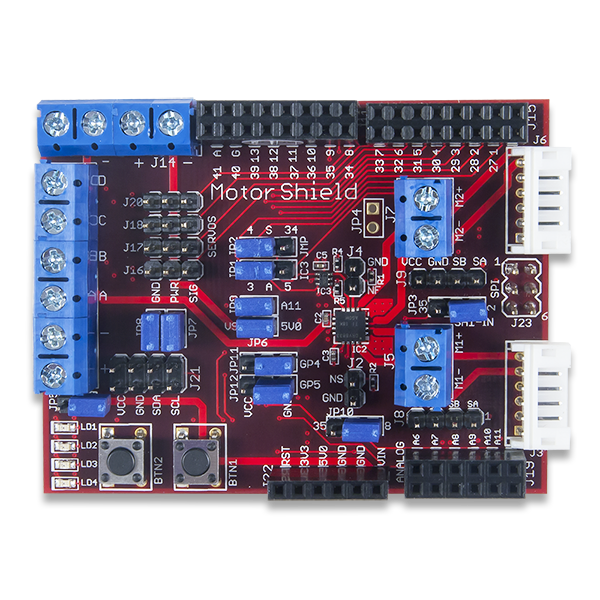
The Motor Shield has the following connectors:
J1: Power Supply for the DC motor driver
This connector provides power to the DVR8833RTY motor driver for the DC motors. Motor supply voltage range is 2.7-10.8 V.
J3 & J6: DC motor 6-pin JST connector
These connections provide power and feedback signals for DC motors. The pin-outs are compatible with the Digilent DC gear-motors.
J5 & J7: DC motor terminal block connector
These connections provide the power supply pin-out for most two wire DC motors.
J2: DC motor driver disable
Shorting these two pins (or driving the NS signal pin low) will put the DC motor driver into sleep mode. This disables the motor driver and therefore reduces power consumption. This option is useful for low power applications.
J4: DC motor driver fault indicator
The NF signal will be driven low when there is a fault detected within the DC motor driver. Possible reasons for fault include overcurrent, overheat, and low voltage.
J8 & J9: DC motor feedback signal headers
Headers for connecting DC motor feedback signals.
J10: Power Supply for Stepper motor
This connector provides power for driving the stepper motor.
J12 & J13: Stepper motor terminal block connectors
These connections are used for driving a stepper motor.
J14: Power Supply for servo motors
This connector provides external power for driving the servo motors. If using this header remove JP6 to ensure that servo power supply is not shorted to the 5 Volt Uno32 power supply.
J11 & J15: Digital Signal Pass-Through Connectors
This connector passes the digital I/O pins on the Uno32 through to the Motor Shield.
J21: I2C #1 Daisy Chain Connector
This is a 2×4 pin header connector that provides access to the I2C signals SDA and SCL as well as power from the 3.3V power bus and ground. This can be used to extend the I2C bus off of the board and to power external I2C devices. Digilent has cables and a selection of I2C peripheral modules that can be accessed using this connector.
J19: Analog Signal Pass-Through Connector
This connector passes the analog input pins on the Uno32 through the Motor Shield.
J22: Power Pass-Through Connector
This connector passes the power connector from the Uno32 through the Motor Shield, and powers the Motor Shield from the Uno32.
2. DC Motor Controller
The Motor Shield provides a means to control 2 independent DC motors via a DRV883 dual H-bridge motor driver. The motor driver must be powered via J1 to operate, voltages between 2.7 and 10.8 volts are acceptable. Each channel is controlled by an “enable” and “direction” signal.
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 46 | Enable1: OC1/RD0 | |
| 4 | 59 | Direction1: RF1 | |
| 3/5 | 46/49 | Enable2: OC1/RD0 or OC2/RD1 | Select with JP1 |
| 4/34 | 59/53 | Direction2: RF1 or PMRD/CN14/RD5 | Select with JP2 |
Channel 2 can be set up for identical or independent operation from channel 1 using JP1 and JP2.
PWM levels on enable pins will regulate the speed of the motors. Logic levels on direction pins will determine the motors rotation direction of the attached DC motors. The Uno32 uses a demultiplexer and pull-down resistors on the inputs to the DRV8833 H-Bridge pins to ensure that the H-Bridge only works in fast decay mode. Table 1 lists the motor responses that result from various input combinations.
| DIR1 | EN1 | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | Stop |
| 0 | 1/PWM | Fprward |
| 1 | 0 | Stop |
| 1 | 1/PWM | Reverse |
| DIR2 | EN2 | Result |
| 0 | 0 | Stop |
| 0 | 1/PWM | Forward |
| 1 | 0 | Stop |
| 1 | 1/PWM | Reverse |
The DRV8833 chip provides overcurrent protection on the motor drive circuits. Each internal drive FET is independently monitored for an overcurrent condition and will be shut down internally to protect the chip. When an overcurrent condition is sensed the chip will shut down the FET with the fault and then set the NFAULT pin low signaling a fault condition on the chip. The remaining FETs will continue to operate as normal. When the fault condition is over, the chip will self-reset and return the NFAULT logic level to logic high. (See Table 2 for connector descriptions.)
There are two Schmitt trigger buffered inputs on connectors J3, J6, J8 and J9 that bring motor speed feedback signals to the controlling system board. The Digilent motor and gearbox have hall-effect sensors arranged in a quadrature encoder format. These buffers have 5V tolerant inputs, when operated at 3.3V.
The quadrature encoder signals are a pair of square waves whose frequency is proportional to motor rotation speed and with the pulses 90 out of phase. You can determine the motor speed with the frequency and motor rotation direction by the phase relationship between the two signals.
3. Stepper Motor Controller
The stepper motor controller has 4 output signals. It is composed of 4 open-drain transistor amplifiers.
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 26 | 60 | A: PMD0/RE0 | |
| 27 | 61 | B: PMD1/RE1 | |
| 28 | 62 | C: PMD2/RE2 | |
| 29 | 63 | D: PMD3/RE3 |
The stepper motor driver can be powered by either VIN, or an external power source connected to J10. If connecting an external power source, JP5 should be removed to prevent shorting the stepper motor voltages to the input voltage of the board.
4. Servo Motors
The Motor Shield has 4 servo motor connections. They can be powered from VCC5V0 or an external power source connected to J14. If connecting an external power source, JP6 should be removed. The voltage of the power source can be measured on analog pin A11 via a resistor divider network (see the schematic for more details).
| Uno32Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 64 | Servo1: PMD4/RE4 | J16 |
| 31 | 1 | Servo2: PMD5/RE5 | J17 |
| 32 | 2 | Servo3: PMD6/RE6 | J18 |
| 33 | 3 | Servo4: PMD7/RE7 | J20 |
5. I2C Bus and Connectors
The Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Interface provides a medium speed (100K or 400K bps) synchronous serial communications bus. The I2C interface provides master and slave operation using either 7 bit or 10 bit device addressing. Each device is given a unique address, and the protocol provides the ability to address packets to a specific device or to broadcast packets to all devices on the bus. Refer to the Microchip PIC32MX3XX data sheet and the PIC32 Family Reference Manual for detailed information on configuring and using the I2C interface.
The PIC32MX320 microcontroller on the Uno32 provides for two independent I2C interfaces. The Motor Shield is designed to provide access to one of these interfaces, I2C #1 (SCL1, SDA1). I2C #1 is accessed through the standard Wire library. Connector J21 provides access to I2C port #1.
Connector J21 can be used to extend the I2C bus off of the board to connect to external I2C devices. This is a standard 2×4 pin header connector with 0.100” spaced pins. It provides access to the I2C signals, SCL1 and SDA1, plus VCC3V3 and ground. The VCC3V3 can be used to power external I2C devices.
The I2C bus uses open collector drivers to allow multiple devices to drive the bus signals. This means that pull-up resistors must be provided to supply the logic high state for the signals. The Motor Shield provides 2.2Kohm pull-up resistors on I2C #1.
Generally, only one set of pull-ups are used on the bus. Jumpers JP7 and JP8 can be used to disable the on-board pull-ups on I2C #1 if a different value is needed or some other device on the bus is providing the pull-ups or if I2C #1 isn’t being used and the pull-ups are interfering with the use of the pins. The on-board pull-ups are enabled by install shorting blocks on JP7 and JP8. Removing the shorting blocks disables the pull-ups.
Digilent has several small I/O modules available that can be connected using the I2C connector. These include a 3-axis accelerometer, 4-channel, 12-bit A/D converter, serial character LCD panel, 3-axis gyroscope, and a real-time clock/calendar. The on-board I/O expander is also controlled via I2C #1.
6. I/O Expander
The Motor Shield contains an I/O expander module that gives access to 4 LEDs, 2 pushbuttons, and 2 jumper-switches. The I/O expander is controlled via I2C #1. The outputs can be easily controlled using the Motor Shield MPIDE library.
CHIPKIT and the CHIPKIT Logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S. and other countries, and are used under license.
Appendix: Motor Shield Pin-out Tables
J1 Pins
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Pin | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1-01 | VM (motor driver power supply) | 2.7-10.8 V | ||
| J1-02 | GND |
J2 Pins
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Pin | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J2-01 | Motor Driver NSLEEP | Pull low to sleep | ||
| J2-02 | GND |
J4 Pins
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Pin | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J4-01 | Motor Driver NFAULT | Goes low on error | ||
| J4-02 | GND |
J3 Pins
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Pin | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J3-01 | SB1-IN | |||
| J3-02 | SA1-IN | |||
| J3-03 | GND | |||
| J3-04 | VCC3V3 | |||
| J3-05 | M1+ | |||
| J3-06 | M1- |
J6 Pins
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Pin | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J6-01 | SB2-IN | |||
| J6-02 | SA2-IN | |||
| J6-03 | GND | |||
| J6-04 | VCC3V3 | |||
| J6-05 | M2+ | |||
| J6-06 | M2- |
J5 Pins
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Pin | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J5-01 | M1+ | |||
| J5-02 | M1+ |
J7 Pins
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Pin | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J7-01 | M2+ | |||
| J7-02 | M2- |
J8 Pins
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Pin | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J8-01 | SA1-IN/ Jumper#3 | See JP3 | ||
| 20/A6 | 13 | J8-02 | SB1-IN/A6 | |
| J8-03 | GND | |||
| J8-04 | VCC3V3 |
J9 Pins
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Pin | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 43 | J9-01 | SA2-IN/IC2/INT2/RD9 | |
| 37 | 55 | J9-02 | SB1-IN/CN16/RD7 | |
| J9-03 | GND | |||
| J9-04 | VCC3V3 |
JP3 Pins
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Pin | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 42 | JP3-01 | IC1/INT1/RD8 | |
| JP3-02 | SB1-IN | Select with jumper | ||
| 35 | 45 | JP3-03 | IC4/PMCS1/PMAI4/INT4/R11 |
J10, J12, and J13 Pins (Stepper Motor Connections)
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Pin | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J10-01 | External V+/VIN | Select with JP5 | ||
| J10-02 | External V-/GND | |||
| 26 | 60 | J12-01 | StepperA/PMD0/RE0 | |
| 27 | 61 | J12-02 | StepperB/PMD1/RE1 | |
| 28 | 62 | J13-01 | StepperC/PMD2/RE2 | |
| 29 | 63 | J13-02 | StepperD/PMD3/RE3 |
J14, J16, J17, J18, and J20 Pins (Servo Motor Connections)
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Pin | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J14-01 | External Vs+/VCC5V0 | Select with JP6 | ||
| J14-02 | GND | |||
| 30 | 64 | J16-01 | PMD4/RE4 | |
| J16-02 | External Vs+/VCC5V0 | |||
| J16-03 | GND | |||
| 31 | 1 | J17-01 | PMD5/RE5 | |
| J17-02 | External Vs+/VCC5V0 | |||
| J17-03 | GND | |||
| 32 | 2 | J18-01 | PMD6/RE6 | |
| J18-02 | External Vs+/VCC5V0 | |||
| J18-03 | GND | |||
| 33 | 3 | J19-01 | PMD7/RE7 | |
| J19-02 | External Vs+/VCC5V0 | |||
| J19-03 | GND |
J21 Pins (I2C)
| Uno32 Pin # | PIC32 Pin # | Pin | Signal | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 46 | 37 | J21-01 | SCL1/RG2 | |
| 46 | 37 | J21-02 | SCL1/RG2 | |
| 45 | 36 | J21-03 | SDA1/RG3 | |
| 45 | 36 | J21-04 | SDA1/RG3 | |
| J21-05 | GND | |||
| J21-06 | GND | |||
| J21-07 | VCC3V3 | |||
| J21-08 | VCC3V3 |